
The argon decreases the rate at which the tungsten filament evaporates by hindering the diffusion of the vaporized metal atoms away from the filament, increasing the probability that they will reattach to the filament.Īrgon is used for producing gas lasers which produce green light. Shells 5 through 7: 32 electrons in any known element, however there are additional orbitals available to hold even more electrons, but there is. Sample Problem 8.3 Ranking Elements by Atomic Size PLAN: SOLUTION: PROBLEM: Using only the periodic table (not Figure 8. It is used in incandescent light bulbs to permit the filament to be heated to a higher temperature, and therefore to produce a whiter light than would be practical in a vacuum. Therefore, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius.Argon is a noble gas which composes about 1% of the atmosphere. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary.

ATOMIC RADIUS OF AR FREE
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. Atomic Radius of Argon The atomic radius of Argon atom is 106pm (covalent radius). The atomic radius of Potassium atom is 203pm (covalent radius). Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. Image showing periodicity of valence s-orbital radius for the chemical elements as size-coded balls on a periodic table grid. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Potassium are 39 41. In the below periodic table you can see the trend of. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Atomic radius of cation is less then its original atom.And anion has larger size then its original atom. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.įor stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A.

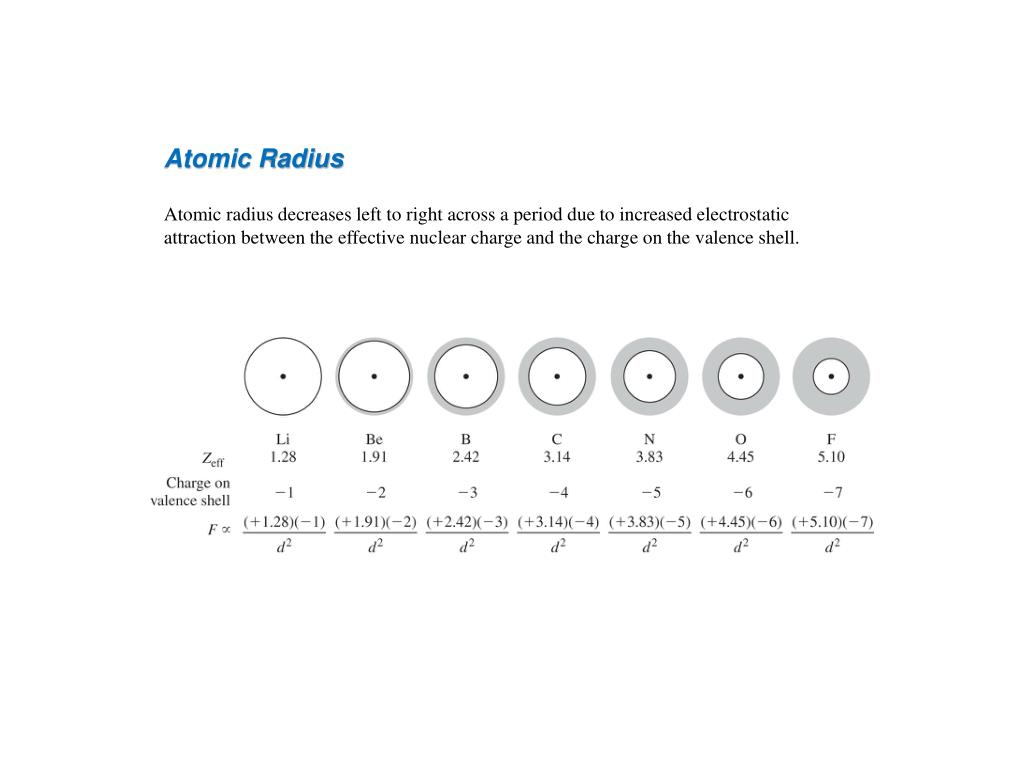
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Sal said that the two ways to calculate the atomic radius are the van der Wall's radius and the covalent radius.But the the covalent radius is usually smaller than the van der Waal's radius as the electron cloud overlap. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs.

Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. Potassium is a chemical element with atomic number 19 which means there are 19 protons in its nucleus. Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in Potassium


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
